
Java is an object-oriented language that was developed in 1995 by James Gosling and it is still one of the most popular languages to develop applications. Spring is a framework for Java application development that provides various libraries. One of the downsides of using Spring is the manual configurations and server setup that can be messy and tiresome even before the actual application development begins. Spring boot is a helper that does the configuration automatically as well as setting up the web server to overcome the downside of the Spring framework. Today we will see how to create a Spring boot project and do some basic settings for development.
List of Contents
Creating a Project
Usint Spring Initializer
Go to the initializer site
Spring Initializr
Initializr generates a spring boot project with just what you need to start quickly!
start.spring.io
Select project, language, name, and dependencies then click Generate

Unzip the downloaded file

Open the file with the editor of your choice

With IntelliJ
Open IntelliJ and click 'New Project'

Select 'Spring Initializr' on the left panel and type in the name, choose 'Java' as the language, choose build type, SDK, a version for Java, and finally package type.

Add dependencies if you need any

Click 'Finish'

Development Environment Set Up
Before we start development we need to check the settings such as the encoding formats.
Encoding Format Settings
Select File -> Settings

Choose Editor -> File Encodings and change the formats on top
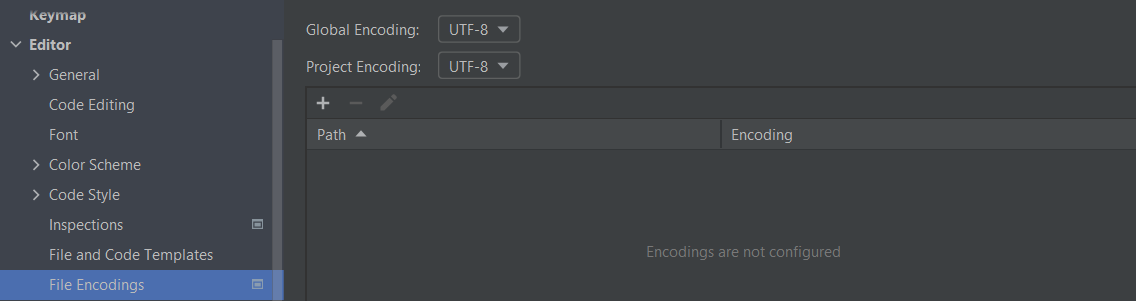
And the bottom (UTF-8 is most commonly used)

JDK Settings
JDK (Java Development Kit) is necessary to develop Java applications and it is often automatically set up when creating a project. To change or manually set up, go to File -> Project Structure

In the opened menu, select the kit

Project Structures
A Spring boot project has the below structure

▶ src/main/java
Java source files
▶ src/main/webapp
Web template, web configurations, static files (image, ...), CSS, JS. Note that you can only use this with war packaging type, not jar
▶ src/main/resources
Application configurations and properties
▶ src/main/resources/application.properties
Default configurations for an application to work are set up automatically. Use this file to change the configurations. Go to the spring.io to check out the property names. Below are some of its properties
▶▷ Core
Set logging level (Loggin level options: TRACE, DEBUG, INFO, WARN, ERROR, FATAL, OFF)
logging.level.org.springframework=DEBUGCreate logging file
logging.file.name=<fileName>.logSets the logging file path
logging.file.name=<fileName>.loglogging.file.path=<path>▶▷ Web
Changes the port (Default: 8080)
server.port=8000Adds a context path (the path that comes after the port)
server.servlet.context-path=/path
Sets session time out time (Default: 30 minutes)
server.servlet.session.timeout=15m▶▷ Security
Changes the user name
spring.security.user.name=adminChanges the password
spring.security.user.password=1234▶▷ Actuator
Adds an endpoint
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=<endpointName>Adds all the endpoints
management.endpoints.web.exposure.include=*Changes the default path (Default: /actuator)
management.endpoints.web.base-path=/newpath▶▷ Data
Connects to DB
spring.datasource.url=<dbPath>Sets DB user
spring.datasource.username=<userName>Sets DB password
spring.datasource.password=<password>▶▷ Integration
▶▷ Devtools
▶▷ Testing
▶ src/test
Unit test codes
Project managers
Spring boot uses a project manager such as Maven or Gradle to fetch all the dependencies needed for an application automatically (jar files for Spring, Hibernate, ... ). Let's have a look at each type's structure
Maven

▶ target
Where compiled files will be stored (Automatically created when the application is run)
▶ mvnw
Maven wrapper file. Runs Maven project (if Maven is not installed on your computer, it will automatically install one. Once Maven is installed, you don't need this file
▶ mvnw.cmd (Window) / mvnw.sh (Linux, Mac)
Maven wrapper file. Once Maven is installed, you don't need this file
▶ pom.xml (Project Object Model file)
A file located in the root that stores the information about the project, dependencies list, and plugins list.
<parent> section defines the default setup such as default compiler level and UTF-8 source encoding. This can be overridden in the <properties> tag
project coordinates
| <groupId> | Group name. The convention is to write the domain name backward |
| <artificialId> | Project name |
| <version> | Project version, append '-SNAPSHOT' when in development |
dependency coordinates
| <groupId> | |
| <artificialId> | |
| <version> | Optional, if omitted, the latest version will be used |
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>3.1.4</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<!-- project information -->
<groupId>com.example</groupId> <!-- project coordinate -->
<artifactId>demo</artifactId> <!-- project coordinate -->
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <!-- project coordinate -->
<packaging>jar</packaging>
<name>demo</name>
<description>demo</description>
<properties>
<java.version>17</java.version>
</properties>
<!-- dependencies -->
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<!-- plugins -->
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>※ For the coordinates for dependencies, visit the sites below. Unlike other sites that only provide one coordinate for a dependency 'maven central repository' provides dependencies that other dependencies depend on
Spring | Home
Cloud Your code, any cloud—we’ve got you covered. Connect and scale your services, whatever your platform.
spring.io
Hibernate. Everything data.
More than an ORM, discover the Hibernate galaxy.
hibernate.org
Maven Central Repository Search
search.maven.org
※ Dependencies such as the spring boot starter that includes multiple dependencies make it hard to check what dependencies are included by just looking at the coordinates in the pom.xml file.
To check what a dependency includes, go to View -> Tool Windows -> Maven

Open the dependencies folder to check

Gradle

In this writing, we have seen how to create a Spring boot project.
'Backend > Java' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Spring Boot Security (1) | 2023.10.01 |
|---|---|
| Spring Boot Actuator (0) | 2023.10.01 |
| Data Persistency Tools (JPA, Hybernate, Mybatis) (3) | 2023.09.09 |
| Spring Boot View Template Tools (0) | 2023.09.02 |
| Spring Boot API (0) | 2023.08.23 |



